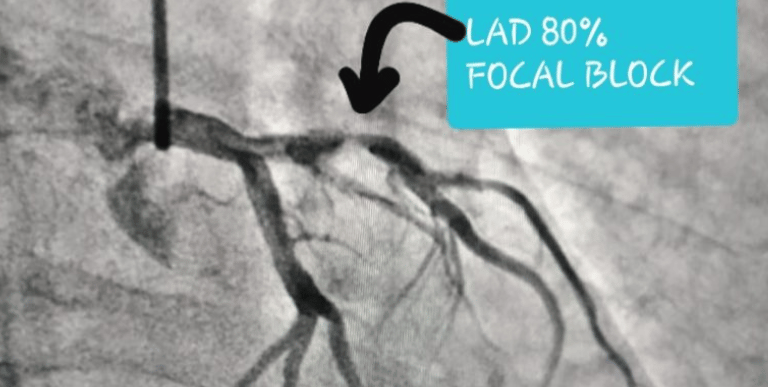
Angiography test is used to find out blockages in coronary arteries. Angiography is the gold standard to diagnose blockage in coronary arteries. In angiography, a contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries through a catheter (plastic thin tube). During this process, doctor watches blood flow in arteries of heart on the X-ray screen. This test is also known as a cardiac angiogram, catheter arteriography or cardiac catheterization. The X-rays provided by an angiography are called angiograms.
Angiograms show the exact location and intensity of heart disease. Angiography is very helpful to Cardiologist to detect severity of coronary artery disease.
Results of an Angiography:
- Angiographic images show exactness and severity of coronary blockages.
- The Angiograms play important role for the Patients with severe heart attack, unexplained heart failure and abnormal chest pain. The Angiograms are very useful to the Cardiologist in deciding treatment and medication type.
- Based on the heart disease, Cardiologist has many treatment options such as balloon angioplasty, coronary stenting and coronary artery bypass surgery or medical management.
An Angiography is safe and it is performed by an expert Cardiologist.
After the successful angiography, generally patient is discharged on the same day. If angiograms results are critical or patient needs immediate treatment, then doctor asks patient to stay in the hospital for further treatment.
How angiography is performed?
- Coronary angiography is performed with the use of local anesthesia and intravenous line. An anesthetic injection is given to the patient to numb the area.
- In angiography procedure, doctor inserts a small catheter gently through the artery either from arm or the groin up to the heart.
- Small amount of contrast dye is injected through the catheter and images are taken.
- X ray images of heart and blood vessels are taken and stored on a computer.
- If coronary arteries are blocked, then cardiologist decides to perform a balloon angioplasty.
- This procedure takes around 20-30 minutes.
- After the procedure, the catheter is removed and the artery in the leg or arm is sealed to stop bleeding with the help of pressure.